Image analysis
Savantic uses deep learning technologies and image analysis within such diverse fields as getting vehicles to discover obstacles and to find signs of lung cancer in X-ray images. We always work together with our clients' domain experts, because we know that they are the ones who best know their own data. This way we can make data collection and modelling more efficient.
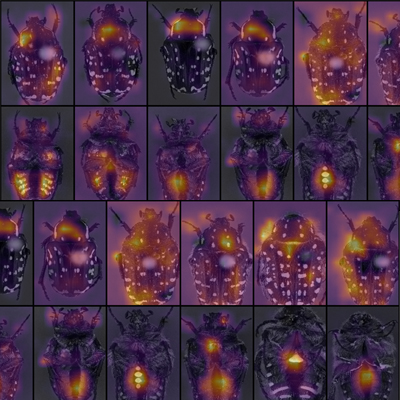
When Miroslav Valan, developer at Savantic, used our technologies for image analysis in his research, presented in his PhD thesis Automated Taxonomic Identification of Insects with Expert-Level Accuracy Using Effective Feature Transfer from Convolutional Networks, it revolutionised insect classification methods, which traditionally is done manually by humans.
We use the same technologies for image and data analysis in projects for the industrial sector, for sensor-equipped vehicles and in medical devices to build AI-based solutions which help create new opportunities and more value for our customers.
Industrial
Image analysis is a powerful tool for digitalising industrial processes like:
Quality assurance
Many processes involve manual steps, where humans check products for defects. Some of the challenges of this type of manual work is that it is expensive, that it becomes a bottleneck in manufacturing speed and that it may lead to defects not being detected.
Humans become tired and quality checks are rarely an exciting work task. By using artificial intelligence or traditional image analysis this production step can be automated.
Tracking and tracing
In order to guarantee quality in manufacturing, it is important to be able to track a product throughout the manufacturing chain. In some cases this can be done using QR codes or bar codes. In other cases those technologies are not a feasible solution. In such cases, using a tracking camera through each step of the process may be a better choice. If a defect is detected, the product can be traced throughout the manufacturing chain, which makes it easier to make improvements to the processes, resulting in higher quality products.
Digital twins
Having a digital copy of a machine or a process step is a big advantage. It makes it possible to quickly assess the entire manufacturing process and to simplify follow-ups by recording all the steps that a product goes through, making testing and simulating process changes easier. Such a copy of a real-world object or process is called a digital twin.
One challenge that we have often seen is that many processes use machines which are not digital, or machines which output poor quality data. By attaching a camera that monitors the machine and then analyse its images, we have been able to create a digital twin without having to replace the machine.
Automotive
The automotive industry is preparing for a revolution brought about by self-driving vehicles. Succeeding in this new automotive landscape requires advanced image analysis techniques, but this is not the only application possible. Here are some automotive projects we have been involved in:
Driver analysis
Today’s vehicles are equipped with a host of intelligent information systems to help the driver drive safely. But we know from research that a driver can not possibly process all the information that a complex traffic situation creates. For this reason, the vehicle attempts to make a selection and present only the information that the driver has not already discovered.
We have, for instance, worked with eye-tracking technology in order to understand what the driver is actually paying attention to, and, based on this, make a decision whether a warning is necessary or not. Another common use case is directing the camera towards the driver to see if he or she seems to be about to fall asleep or is becoming less focused.
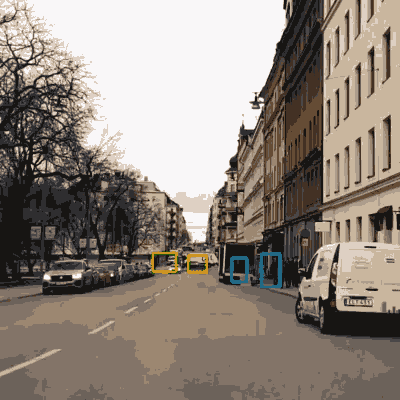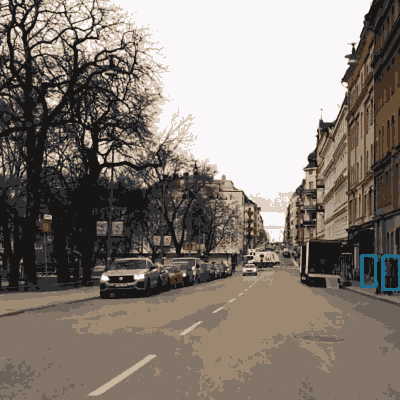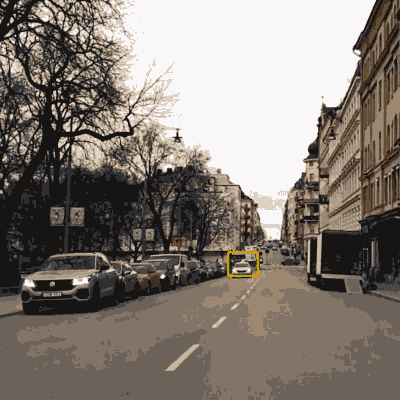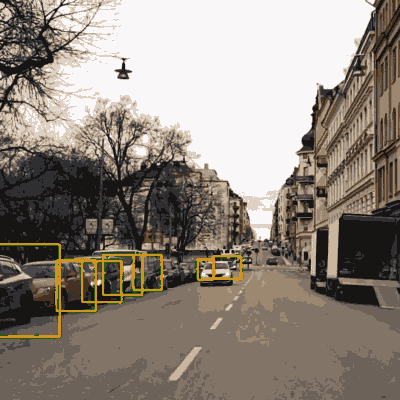
Vehicle surroundings analysis
The standard example here would of course be analysing the environment to make autonomous driving possible. Such driving demands a number of specialised solutions for image analysis for different problems, like scanning road signs.
Outward-facing cameras can also be used for a number of other analysis types, like identifying leaning signs, potholes or wrongly parked cars. This kind of information can be used by a city for planning maintenance or building new parking lots.
Late sensor fusion
Vehicles are equipped with a large number of sensors, not only cameras. At Savantic, we have been involved in projects using what is called late sensor fusion. This means combining signals from different types of sensors in order to make a better assessment of a particular traffic situation. Moving the intelligence from the sensors to different sets of combined raw data improves the quality of the analysis. It is also possible to combine data from different vehicles to create a better overview of a traffic situation. By doing so, the vehicle which receives a particular input can use it to alert another vehicle.
MedTech
Within MedTech, image analysis is often used for diagnosis or to analyse medical samples. We have years of experience from working with this kind of solutions:
Sample analysis
Most of our MedTech projects are about analysing samples or X-ray images. The most well-known application is scanning X-ray images to identify instances of cancer. But this technology can be used in many different areas, such as analysing biopsies, blood samples, bacterial cultures, rashes and skin cancer.
When a sample is sent to a laboratory it is often analysed in a microscope, sometimes manually by medically trained staff, who count the number of cells of a certain type. With image analysis, results can be reported much faster and a greater number of samples can be analysed within a given amount of time. And since lighting, lenses and other equipment can be checked in a laboratory environment, the quality of the analyses can be greatly improved.
Surgery
Robots carrying out some surgery tasks is becoming increasingly common. Image analysis is an important element in such applications. We have also worked with supportive image analysis, where the same technology is used during surgery for keeping track of surgical instruments.

